http://www.benzenecausescancer.info/home/benzene-in-medicine
Has anybody studied how benzene or its derivatives affect the body when they are ingested in these popular medications?
Benzene and benzene-based molecules are part of many popular medications used to relieve pain, alleviate cold and flu symptoms, and as a weight-loss aid. We know that benzene is a human carcinogen with a unique electromagnetic potential that enables it to insert itself into human DNA. So why is it being used in these popular medications?
Provided below is detailed information about:
- Decongestants contain benzene
- Many pain relievers contain benzene or benzene derivatives
________________________________________ |
U.S. Food and Drug Administration recalls another pain reliever that contains a benzene derivative
Decongestants contain benzene
Until recently, phenylpropanolamine (PPA), which contains benzene, has been used in decongestants. It works by narrowing blood vessels, which clears nasal congestion but may also cause an increase in blood pressure in some patients. PPA also temporarily decreases appetite.
In November 2000, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a public health warning for PPA. Based on results of a research program, the FDA requested that manufacturers voluntarily discontinue marketing products that contain PPA because these products increased the incidence of strokes. In response to the FDA’s request, many companies have voluntarily reformulated their products to exclude PPA. The FDA is not maintaining a comprehensive, updated list of products that still contain PPA, so check the label before using these medications.
________________________________________ |
- Molecular structure of PPA
- Chemical name: Benzene- methanol, cx-(1-aminoethyl)-, hydrochloride
Could the benzene ring in the PPA molecule be responsible for
the health risks associated with using these products?
Many pain relievers contain benzene or benzene derivatives
Many pain relievers (known as analgesics) contain benzene or a derivative of benzene, which is produced when one of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by another molecule. Analgesic drugs include the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs such as aspirin, naproxen, ibuprofen, acetaminophen, celecoxib, rofecoxib, and valdecoxib are used to relieve pain and to reduce fever and inflammation.
________________________________________ |
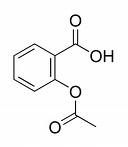
Aspirin
The molecular structure of aspirin is shown at right. Note its benzene derivative.
Aspirin is often used to alleviate minor pains and aches, fever, and inflammation. It has also an anticoagulant (blood thinning) effect and is used in long-term low-doses to prevent heart attacks.
|
|
 |
________________________________________ |
Naproxen
The molecular structure of naproxen is shown at right. Note its two benzene rings.
|
|
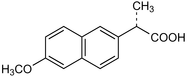 |
Naproxen (trade names: Aleve, Anaprox, Naprosyn, Naprelan) is commonly used to treat pain, fever, inflammation, and stiffness caused by arthritis, gout, injury, menstrual cramps, tendinitis, and bursitis. It works by reducing hormones that cause inflammation and pain in the body.
In December 2004, the FDA issued a press release following the decision by the National Institutes of Health to halt a five-year study, called the Alzheimer's Disease Anti-Inflammatory Prevention Trial. That study aimed to test both Aleve and Celebrex as preventatives for Alzheimer's disease. Preliminary information from the study showed naproxen elevated the risk of heart attack and stroke by 50 percent.
________________________________________ |
Ibuprofen
The molecular structure of ibuprofen is shown at right. Note its benzene derivative.
|
|
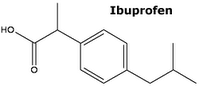 |
Ibuprofen, used as a painkiller especially where there is inflammation, is used widely to relieve headache pain. It is also used to treat general pain arising from injuries (such as sporting injuries), illnesses (such as influenza, shingles, gout), and post-operative pain. It is widely marketed under various trade names including Brufen, Advil, Nurofen, Motrin, Nuprin, and Act-3.
________________________________________ |
Acetaminophen
The molecular structure of acetaminophen is shown at right. Note its benzene derivative.
|
|
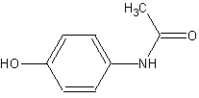 |
Acetaminophen, also called Paracetamol, is a popular analgesic that is used to relieve fever, headaches, and other minor aches and pains. It is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu medications and many prescription analgesics. It is remarkably safe in standard doses, but because of its wide availability, deliberate or accidental overdoses are not uncommon.
Paracetamol, unlike other common analgesics such as aspirin and ibuprofen, has no anti-inflammatory properties, and so it is not a NSAID. In normal doses paracetamol does not irritate the lining of the stomach nor affect blood coagulation, the kidneys or the fetal ductus arteriosus (as NSAIDS can).
________________________________________ |
Celecoxib
The molecular structure of celecoxib is shown at right. Note its benzene derivatives.
|
|
 |
Celecoxib is best known by the brand name Celebrex. Celecoxib is used to treat osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute pain, painful menstruation, and to reduce colon and rectum polyps.
On December 17, 2004, Pfizer announced that in a National Cancer Institute study, those taking high doses of celecoxib (higher than the FDA-approved dose range) had increased risk of a heart attack or stroke than those taking placebo. On April 7, 2005, the FDA asked manufacturers of all marketed prescription NSAIDs, including Celebrex, a COX-2 selective NSAID, to revise the labeling for their products to include a warning highlighting the potential for increased risk of cardiovascular events and the well described, serious, potential life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeding associated with their use.
________________________________________ |
Rofecoxib
The molecular structure of rofecoxib is shown at right. Note its two benzene derivatives.
|
|
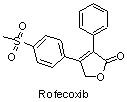 |
Rofecoxib is a prescription NSAID that was used in the treatment of osteoarthritis, acute pain, and dysmenorrhoea. Formerly marketed under the trade names Vioxx, Ceoxx and Ceeoxx, it was voluntarily withdrawn from the market in 2004 because of concerns about increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Rofecoxib was one of the most widely used drugs ever to be withdrawn from the market. Worldwide, over two million people were prescribed Vioxx at
________________________________________ |
Valdecoxib
The molecular structure of rvaldecoxib is shown at right. Note its two benzene derivatives.
|
|
 |
Valdecoxib is a prescription NSAID, marketed as Bextra, used in the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and painful menstruation and menstrual symptoms. On April 7, 2005, the manufacturer, Pfizer, withdrew Bextra from the US market on recommendation by the FDA. Common risks associated with the drug include angina, heart attack, stroke, fatal skin reactions, and Stevens Johnson syndrome.
________________________________________ |
http://www.benzenecausescancer.info/home/benzene-in-medicine
|